Unleashing the Power of Cloud Computing: Empowering Businesses with Scalability and Efficiency
Cloud Computing: Empowering Businesses with Scalability and Efficiency
In today’s digital age, businesses are constantly seeking ways to enhance their operations, streamline processes, and stay ahead of the competition. One revolutionary technology that has transformed the business landscape is cloud computing. With its ability to offer scalable and efficient solutions, cloud computing has become an indispensable tool for businesses of all sizes.
So, what exactly is cloud computing? In simple terms, it refers to the delivery of on-demand computing resources over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal computers for data storage and processing, businesses can now leverage remote servers hosted in secure data centers.
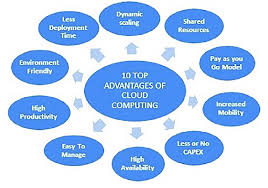
One of the key advantages of cloud computing is its scalability. With traditional infrastructure, businesses often face limitations when it comes to expanding their IT capabilities. Hardware upgrades can be costly and time-consuming. However, with cloud computing, businesses can easily scale their resources up or down based on their needs. Whether it’s increasing storage capacity or adding more processing power, the cloud offers flexibility that was once unimaginable.
Moreover, cloud computing offers significant cost savings for businesses. By eliminating the need for physical infrastructure and reducing maintenance costs associated with in-house servers, companies can redirect their resources towards other critical areas of their operations. Additionally, pay-as-you-go models allow businesses to pay only for the resources they use, further optimizing cost-efficiency.
Security is another crucial aspect that businesses consider when adopting new technologies. Cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches. These providers employ encryption techniques and implement stringent access controls to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Collaboration and remote work have become increasingly important in today’s interconnected world. Cloud computing enables seamless collaboration among teams located in different geographical locations by providing a centralized platform accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This empowers employees to work together efficiently while accessing real-time information and documents.
For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), cloud computing offers a level playing field by providing access to enterprise-level technologies without the need for substantial upfront investments. SMEs can now leverage the same powerful tools and resources as their larger counterparts, allowing them to compete more effectively in the market.
The benefits of cloud computing extend beyond businesses. Cloud-based applications and services have revolutionized various industries, including healthcare, education, finance, and entertainment. From telemedicine platforms to e-learning systems, cloud computing has enabled innovation and transformed the way these industries operate.
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, cloud computing will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping the future of businesses worldwide. Its ability to provide scalability, cost-efficiency, enhanced security, and seamless collaboration makes it an essential tool for organizations striving for success in the digital era.
In conclusion, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer for businesses looking to stay agile and competitive. By harnessing its power, companies can unlock new opportunities for growth while optimizing their operations. The scalability, cost-efficiency, security features, and collaborative capabilities offered by cloud computing make it a must-have technology in today’s ever-evolving business landscape.
Commonly Asked Questions about Cloud Computing in the UK
- What are the 3 types of cloud computing?
- What are the 4 types of cloud computing?
- What is cloud computing and how it works?
- What is cloud computing with example?
What are the 3 types of cloud computing?
The three main types of cloud computing are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers businesses the flexibility to rent virtual machines, storage, and networks on a pay-as-you-go basis. With IaaS, organizations can focus on managing their applications and data without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is a cloud computing model that provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. It offers tools and services to streamline the development process, making it easier for businesses to create and deploy scalable applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is a cloud computing model where software applications are delivered over the internet on a subscription basis. With SaaS, users can access and use software applications without having to install or maintain them locally. This model allows businesses to leverage powerful software solutions without the need for extensive hardware or software management.
Each type of cloud computing offers different levels of control and flexibility, catering to various business needs and requirements. Organizations can choose the most suitable type based on their specific goals, resources, and IT capabilities.
What are the 4 types of cloud computing?
There are generally four types of cloud computing models, each offering different levels of control, flexibility, and management options. These models are:
- Public Cloud: Public cloud computing is the most common type and is provided by third-party service providers. In this model, resources such as servers, storage, and applications are shared among multiple organizations or users over the internet. It offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use since the infrastructure is managed by the provider. Examples of public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Private Cloud: Private cloud computing involves dedicated infrastructure that is exclusively used by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or in a data center managed by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer enhanced security and control over data since they are not shared with other organizations. They are suitable for businesses with strict compliance requirements or those needing greater customization and control over their infrastructure.
- Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud computing combines elements of both public and private clouds to create a hybrid environment tailored to specific business needs. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both models while maintaining flexibility in managing workloads across multiple platforms. For instance, sensitive data can be stored in a private cloud while utilizing the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public cloud resources for less critical applications.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud computing refers to the use of multiple public cloud providers simultaneously to meet specific requirements or avoid vendor lock-in. Organizations may choose different providers based on factors such as pricing, geographical coverage, specialized services, or performance optimization. By spreading workloads across various clouds, businesses can achieve redundancy, minimize downtime risks, and optimize resource allocation.
Each type of cloud computing model offers distinct advantages and considerations based on an organization’s requirements regarding security, compliance, scalability, budget constraints, and desired level of control over their infrastructure. Understanding these options allows businesses to make informed decisions when adopting cloud computing technologies.
What is cloud computing and how it works?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, software, and networking, over the internet. It allows businesses and individuals to access and use these resources on-demand without the need for owning or managing physical infrastructure.
The underlying technology behind cloud computing involves a network of remote servers hosted in data centers. These servers are responsible for storing and processing data and running applications. When users require computing resources, they connect to the cloud service provider’s network via the internet.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how cloud computing works:
Cloud Service Providers: Companies that offer cloud services are known as cloud service providers (CSPs). Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. These CSPs own and manage the physical infrastructure required for cloud computing.
Data Centers: CSPs operate multiple data centers worldwide. These data centers house numerous servers that store data and run applications. They are designed with redundancy and high availability in mind to ensure uninterrupted service.
Virtualization: Virtualization is a key technology used in cloud computing. It allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) or containers to run on a single physical server simultaneously. Each VM operates independently, providing isolation between different users or applications.
Service Models: Cloud computing offers different service models based on user requirements:
– Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Users have access to virtualized hardware resources such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure.
– Platform as a Service (PaaS): Users can develop, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
– Software as a Service (SaaS): Users can access software applications over the internet without needing to install or maintain them locally.
Deployment Models: Cloud computing also offers various deployment models:
– Public Cloud: Resources are owned and operated by third-party CSPs who make them available to the public over the internet.
– Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. It offers enhanced security and control but requires additional management.
– Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private cloud resources, allowing organizations to utilize both based on their specific needs. This provides flexibility and scalability while maintaining control over sensitive data.
Accessing the Cloud: Users access cloud resources through web browsers, desktop applications, or mobile apps provided by the CSPs. They authenticate themselves and connect securely to the cloud environment via the internet.
Scalability and Elasticity: One of the key advantages of cloud computing is its ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. Users can easily increase or decrease computing power, storage capacity, or network bandwidth as needed, paying only for what they use.
Security and Data Protection: Cloud service providers implement robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations. Encryption techniques, firewalls, access controls, and regular backups are employed to enhance security.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate by providing flexible, cost-effective, and scalable solutions that eliminate the need for extensive physical infrastructure management. It has become an essential technology in today’s digital world, enabling innovation, collaboration, and efficient resource utilization for organizations of all sizes.
What is cloud computing with example?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, providing users with on-demand access to a wide range of resources such as storage, processing power, and software applications. These services are hosted on remote servers and accessed through a web browser or specific applications.
Here are a few examples of cloud computing in action:
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is a popular cloud computing model where software applications are hosted by a provider and made available to users over the internet. Examples include online productivity tools like Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), customer relationship management (CRM) systems like Salesforce, and collaboration platforms like Microsoft Office 365.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure over the internet. Instead of purchasing physical servers and managing them on-site, businesses can rent these resources from cloud providers. Leading IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a development environment in the cloud that allows developers to build, test, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. It provides tools and frameworks for application development, database management systems, and other necessary components. Examples of PaaS include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service.
- Storage as a Service: Cloud storage services allow users to store their files securely in remote data centers accessible via the internet. Providers like Dropbox or Google Drive offer scalable storage solutions that can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions provide businesses with off-site backup and recovery options for their critical data and applications. By storing backups in the cloud instead of relying solely on local backups, companies can ensure business continuity even in the event of hardware failures or natural disasters.
These examples illustrate how cloud computing has transformed various aspects of technology and business operations. By leveraging the power of the cloud, organizations can access scalable resources, reduce infrastructure costs, enhance collaboration, and focus on their core competencies while leaving the management of underlying infrastructure to trusted cloud service providers.