Unleashing the Power of Cloud Infrastructure Services: Empowering Businesses in the Digital Age
Unleashing the Power of Cloud Infrastructure Services: Empowering Businesses in the Digital Age
Cloud Infrastructure Services: Empowering Businesses in the Digital Age
In today’s digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and improve overall efficiency. One solution that has revolutionized the way organizations operate is cloud infrastructure services. With its numerous benefits and capabilities, cloud infrastructure services have become an essential component of modern business strategies.
Cloud infrastructure services provide businesses with a flexible and scalable platform for storing, managing, and accessing data and applications. Instead of relying on physical servers located on-site, cloud infrastructure allows businesses to leverage virtual servers hosted in secure data centers. This shift to the cloud offers a wealth of advantages that can transform the way businesses operate.
Scalability is one of the key benefits of cloud infrastructure services. Traditional IT infrastructures often require significant investments in hardware and software, which can be costly and time-consuming to upgrade or expand. With cloud infrastructure services, businesses have the ability to scale their resources up or down based on their needs. Whether it’s increasing server capacity during peak periods or reducing resources during slower times, cloud infrastructure allows for seamless scalability without any major disruptions.
Another advantage of cloud infrastructure services is enhanced reliability and uptime. Cloud service providers typically offer robust data centers with redundant systems that ensure high availability and minimize downtime. This means businesses can rely on a stable and resilient infrastructure that keeps their critical applications running smoothly without interruption.
Cost-effectiveness is another compelling reason why many businesses are turning to cloud infrastructure services. By shifting from a capital expenditure model (CAPEX) to an operational expenditure model (OPEX), organizations can reduce upfront costs associated with hardware purchases, maintenance, and upgrades. Cloud service providers handle the management and maintenance of the underlying infrastructure, allowing businesses to focus more on their core competencies while enjoying predictable monthly expenses.
Security is a top concern for any business when it comes to storing sensitive data and applications in the cloud. Cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures, employing advanced encryption techniques, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard data from unauthorized access. Additionally, cloud infrastructure services often include built-in backup and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring that businesses can quickly recover their data in the event of an unforeseen incident.
Collaboration and remote accessibility are also greatly enhanced through cloud infrastructure services. With data stored in the cloud, employees can access files and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This enables seamless collaboration among team members working remotely or across different locations, increasing productivity and efficiency.
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, cloud infrastructure services have become a critical enabler of growth and innovation. By leveraging the power of the cloud, organizations can focus on their core competencies while relying on a secure, scalable, and cost-effective infrastructure. Whether it’s a small startup or a large enterprise, cloud infrastructure services offer immense potential for businesses to thrive in the increasingly competitive digital landscape.
In conclusion, cloud infrastructure services have revolutionized the way businesses operate by providing flexible scalability, enhanced reliability, cost-effectiveness, robust security measures, improved collaboration capabilities, and remote accessibility. As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, embracing cloud infrastructure services has become essential for organizations seeking to stay ahead in today’s digital age.
Commonly Asked Questions about Cloud Infrastructure Services in the UK
- What is the role of cloud infrastructure services?
- What is cloud infrastructure example?
- What are the 3 basic cloud services?
- What are the cloud infrastructure services?
What is the role of cloud infrastructure services?
The role of cloud infrastructure services is to provide businesses with a virtual platform for storing, managing, and accessing their data and applications. These services replace or augment traditional on-premises IT infrastructure, such as physical servers and storage systems, with virtualized resources hosted in secure data centers.
Cloud infrastructure services play several key roles in empowering businesses:
- Scalability: Cloud infrastructure services allow businesses to scale their resources up or down based on their needs. This flexibility enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing demands, whether it’s handling increased traffic during peak periods or reducing resources during slower times.
- Reliability and uptime: Cloud service providers typically offer robust data centers with redundant systems that ensure high availability and minimize downtime. By leveraging these services, businesses can rely on a stable and resilient infrastructure that keeps their critical applications running smoothly without interruption.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud infrastructure services operate on an operational expenditure (OPEX) model rather than a capital expenditure (CAPEX) model. This means businesses can avoid significant upfront investments in hardware and maintenance costs. Instead, they pay for the resources they use on a subscription basis, allowing for more predictable monthly expenses.
- Security: Cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access. They employ advanced encryption techniques, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information stored in the cloud.
- Collaboration and accessibility: Cloud infrastructure services enable seamless collaboration among team members working remotely or across different locations. With data stored in the cloud, employees can access files and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
- Disaster recovery and backup: Many cloud infrastructure services include built-in backup and disaster recovery capabilities. This ensures that businesses can quickly recover their data in the event of an unforeseen incident such as hardware failure or natural disasters.
Overall, cloud infrastructure services play a crucial role in enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of virtualization, scalability, reliability, cost-effectiveness, security, collaboration, and accessibility. By leveraging these services, organizations can focus on their core competencies while relying on a flexible and robust infrastructure that supports their growth and innovation in the digital age.
What is cloud infrastructure example?
An example of cloud infrastructure is a public cloud service provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These providers offer a range of cloud infrastructure services that businesses can leverage to store, manage, and access their data and applications.
For instance, AWS provides services such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for virtual server hosting, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) for scalable object storage, and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for creating isolated virtual networks. These services form the building blocks of cloud infrastructure and allow businesses to deploy their applications and resources in a flexible and scalable manner.
Similarly, Microsoft Azure offers services like Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure Virtual Networks. GCP provides services such as Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, and Google Virtual Private Cloud.
These cloud infrastructure examples demonstrate how businesses can leverage the resources and capabilities offered by public cloud service providers to build their IT infrastructure without the need for physical servers or on-premises data centers. By utilizing these services, organizations can benefit from scalability, reliability, cost-effectiveness, security measures, and other advantages provided by the cloud.
What are the 3 basic cloud services?
The three basic cloud services are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It allows businesses to rent virtual servers, storage, and networking infrastructure from a cloud service provider. With IaaS, organizations have the flexibility to scale their infrastructure up or down based on their needs without the need for physical hardware investments. Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It offers a complete development environment that includes operating systems, programming languages, databases, and other tools necessary for application development. PaaS allows developers to focus on writing code and designing applications rather than managing hardware or software infrastructure. Popular PaaS providers include Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, and Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of installing and maintaining software on individual devices or servers, users can access applications through web browsers or dedicated client software. SaaS eliminates the need for users to handle software updates or maintenance tasks as those responsibilities lie with the service provider. Examples of widely used SaaS applications include Salesforce CRM, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace (formerly G Suite).
These three basic cloud services provide businesses with different levels of abstraction and control over their IT infrastructure and applications. Organizations can choose the most suitable service model based on their specific requirements and preferences while leveraging the benefits of cloud computing such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and reduced management overheads.
What are the cloud infrastructure services?
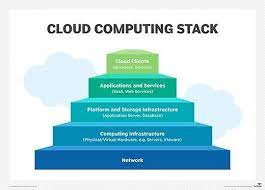
Cloud infrastructure services refer to the range of resources and capabilities provided by cloud service providers to support the storage, management, and processing of data and applications in the cloud. These services typically include:
- Virtual Servers: Cloud infrastructure services offer virtual servers, also known as virtual machines (VMs), which allow businesses to run their applications and software without the need for physical servers. These VMs can be easily provisioned, scaled up or down, and managed through a web-based interface.
- Storage: Cloud infrastructure services provide scalable storage solutions that allow businesses to store and access their data securely in the cloud. This includes options such as object storage for unstructured data, block storage for structured data, and file storage for file-based workloads.
- Networking: Cloud service providers offer networking capabilities that enable businesses to connect their cloud resources securely. This includes virtual private networks (VPNs), load balancers for distributing traffic across multiple servers, and content delivery networks (CDNs) for faster content delivery.
- Databases: Cloud infrastructure services provide database solutions that allow businesses to store, manage, and query their structured data efficiently in the cloud. This includes relational databases (SQL) as well as NoSQL databases for handling unstructured or semi-structured data.
- Content Delivery: Cloud infrastructure services often include content delivery capabilities through CDNs. CDNs help deliver web content and media files quickly by caching them on servers located closer to end-users geographically.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM services offered by cloud providers enable businesses to manage user access rights, permissions, and authentication across their cloud resources securely.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Cloud infrastructure services often include monitoring tools that provide insights into resource utilization, performance metrics, and system health. Additionally, analytics capabilities help businesses derive valuable insights from their data through tools like machine learning algorithms or big data analytics platforms.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Cloud infrastructure services typically provide built-in backup and disaster recovery solutions. These services ensure that businesses can recover their data and systems in the event of a failure or disaster, minimizing downtime and data loss.
- Security Services: Cloud providers offer various security services to protect data and applications stored in the cloud. This includes encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, vulnerability scanning, and identity protection measures.
- Compliance and Governance: Cloud infrastructure services often include features that help businesses meet regulatory compliance requirements and enforce governance policies. This includes auditing tools, access controls, and compliance certifications.
These are just some of the common cloud infrastructure services available to businesses. The specific offerings may vary depending on the cloud service provider and the needs of the organization.
Latest articles
- Discover the Top Project Management Software Solutions for Your Business
- Unlocking Team Efficiency with Atlassian Jira Software
- Unlocking Efficiency: The Asta Powerproject Advantage in Construction Project Management
- The Essential Role of an Assistant Project Manager in Project Success
- Unlocking Project Success with PMBOK: A Guide to Effective Project Management
Latest comments
Categories
- acronis
- ad agency
- adobe
- ads marketing
- affiliate marketing
- agency web
- agile
- agile project management
- analytics cloud
- apm
- app
- apps
- asana
- assistant
- assistant manager
- associate
- association of project management
- asta
- atlassian
- business advisory
- business consultant
- business consulting
- business services
- certificate courses
- certificate programs
- cloud
- cloud computing
- cloud hosting
- cloud linux
- cloud platform
- cloud server
- cloud web hosting
- company services
- computer
- computer course
- computing
- construction
- construction management
- consulting companies
- consulting firms
- consulting services
- cost management
- customizable
- data platform
- development
- digital agencies
- digital agency
- digital marketer
- digital marketers
- digital marketing
- digital marketing agencies
- digital marketing agency
- digital marketing companies
- digital marketing company
- digital marketing service
- digital marketing services
- digital strategy
- digitalmarketer
- engine
- free
- github
- google cloud
- google cloud platform
- greencloud
- iaas
- infrastructure as a service
- internet
- internet marketing
- internet marketing agency
- internet marketing company
- internet marketing firm
- internet marketing service
- internet marketing services
- internet media marketing
- internet of things
- jira
- junior
- lean
- lean projects
- leeds
- linux
- linux hosting
- london
- management
- management consultant
- management course
- management courses
- management jobs
- management skills
- management training courses
- manager
- manager jobs
- manager tools
- marketing
- marketing agency
- marketing cloud
- marketing companies
- marketing management
- marketing manager
- marketing manager software
- marketing pr
- marwick internet marketing
- media agency
- media services company
- microsoft
- monitoring tools
- mybusiness
- network security
- nottingham
- office manager
- online agency
- online backup
- online marketing
- online marketing agency
- online marketing company
- online marketing firm
- paas
- planning
- pm p
- pmbok
- pmi
- pmi certification
- pmp
- pmp certification
- pr agencies
- pr agency
- pr communications
- pr firm
- price
- prince2
- prince2 foundation
- productivity software
- program manager
- project management
- project management jobs
- project management software
- project management system
- project manager
- project planning
- project planning software
- project tracking
- project tracking software
- saas
- search engine marketing
- search marketing
- security course
- security courses
- security jobs
- sem
- seo
- service cloud
- service manager
- service marketing
- services
- services marketing
- small
- small business marketing companies
- social media
- software developer
- software engineer
- task
- task management
- task management software
- tech solutions
- technology consulting
- telecom
- thingful
- trello
- uk
- Uncategorized
- vmware
- vps
- vps server
- web application
- web hosting
- web hosting services
- web server
- webhost
- website
- website hosting
- zoho
- zoho projects