Exploring the Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Cloud Computing
Understanding IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
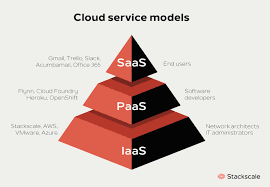
In the realm of cloud computing, there are three primary service models that businesses can leverage to meet their IT infrastructure and application needs. These models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. With IaaS, businesses can rent IT infrastructure such as servers, storage, and networking on a pay-as-you-go basis. This model allows for scalability and flexibility, as businesses can easily adjust their resource allocation based on their needs.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. This model provides tools and services to streamline the development process and accelerate time-to-market for applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications through web browsers without the need for installation or maintenance. SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to manage software updates and infrastructure maintenance, making it a cost-effective solution for many organisations.
Each of these cloud service models offers unique benefits and caters to different business requirements. By understanding the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, businesses can make informed decisions about which model best suits their needs.
Key Advantages of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Scalability, Cost Efficiency, and Enhanced IT Flexibility
- Scalability
- Cost-Effective
- Cost-Effective Licensing Model
- Scalability
- Reduced IT Overhead
- Cross-Device Compatibility
Three Key Concerns of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Cost Escalation, Provider Dependency, and Data Security Risks
- Costs can escalate if resources are not optimally allocated
- Dependency on the platform provider for updates and maintenance
- Data security concerns due to storing sensitive information off-site
Scalability
One significant advantage of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) is their scalability feature, allowing businesses to effortlessly adjust their IT resources according to fluctuating demand. Whether it’s increasing server capacity during peak periods or reducing storage space during quieter times, the scalability of these cloud service models enables organisations to efficiently manage their resources and costs, ensuring optimal performance and flexibility in meeting business needs.
Cost-Effective
One significant advantage of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) is their cost-effectiveness. With these cloud service models, businesses can pay only for the resources they use, eliminating the need for large upfront investments in infrastructure or software. This pay-as-you-go approach allows companies to scale their resources based on demand, optimising costs and ensuring efficient resource allocation. By reducing upfront costs and offering flexible pricing structures, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS enable businesses to access cutting-edge technology solutions without breaking the bank.
Cost-Effective Licensing Model
One significant advantage of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) is their cost-effective licensing model. With these cloud service models, businesses can benefit from a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based pricing structure, eliminating the need for upfront investments in expensive hardware or software licenses. This flexible approach allows companies to scale their IT resources according to their needs, resulting in cost savings and improved budget management. Additionally, the cost-effective licensing model of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS enables businesses to access the latest technology and software updates without incurring additional expenses, ensuring they remain competitive in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Scalability
Scalability is a significant advantage offered by Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) models in cloud computing. With these cloud service models, businesses have the flexibility to scale their resources up or down based on demand. This scalability feature allows companies to efficiently manage their IT infrastructure, applications, and services without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware or software. Whether it’s expanding storage capacity, increasing computing power, or accommodating more users, the scalability of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS ensures that businesses can adapt to changing needs quickly and cost-effectively.
Reduced IT Overhead
One significant advantage of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) is the reduced IT overhead they offer to businesses. By leveraging these cloud service models, organisations can offload the burden of managing and maintaining complex IT infrastructure, platforms, and software applications. This reduction in IT overhead allows businesses to focus their resources and efforts on core activities and strategic initiatives, leading to increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved overall productivity.
Cross-Device Compatibility
Cross-Device Compatibility is a significant advantage offered by Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) models. With cross-device compatibility, users can access their infrastructure, applications, and software from various devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones seamlessly. This flexibility ensures that users can work efficiently and access essential resources regardless of their location or the device they are using. It enhances productivity and collaboration among teams by enabling easy access to resources across different devices, making IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS models highly versatile and user-friendly.
Costs can escalate if resources are not optimally allocated
One significant drawback of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) is the potential for costs to escalate if resources are not optimally allocated. Without careful monitoring and management of resource usage, businesses may end up paying for more resources than they actually need, leading to unnecessary expenses. It is essential for organisations to closely track their resource consumption and adjust their allocation accordingly to avoid cost escalation and ensure cost-effectiveness in leveraging cloud services.
Dependency on the platform provider for updates and maintenance
An important drawback of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) is the dependency on the platform provider for updates and maintenance. While these cloud service models offer convenience and cost-effectiveness, businesses relying on them relinquish control over the timing and execution of updates, patches, and overall maintenance. This dependency can lead to potential disruptions in service delivery if the provider experiences downtime or delays in implementing critical updates, highlighting the importance of carefully considering the level of control and responsibility that businesses are willing to cede to their service providers when opting for cloud-based solutions.
Data security concerns due to storing sensitive information off-site
Data security concerns arise with IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS due to the storage of sensitive information off-site. Entrusting valuable data to external cloud service providers raises apprehensions about data privacy, confidentiality, and compliance with regulatory standards. Businesses may worry about the potential risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, or loss of control over their critical information when it is stored outside their direct supervision. Addressing these concerns requires robust security measures, encryption protocols, and stringent access controls to safeguard sensitive data and mitigate the inherent risks associated with off-site storage in cloud environments.