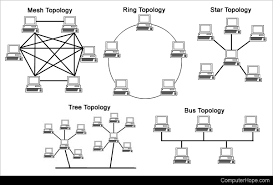
Unleashing the Power of Networks: Connecting People, Resources, and Ideas
Networks: Connecting the World
In today’s digital age, networks have become an integral part of our lives. Whether it’s the internet that connects us globally or the local area networks (LANs) that keep our offices running smoothly, networks play a crucial role in facilitating communication and information exchange.
At its core, a network is a collection of interconnected devices, such as computers, servers, routers, and switches. These devices are linked together through various mediums, including wired (Ethernet cables) or wireless (Wi-Fi) connections. The primary purpose of a network is to enable these devices to communicate with one another and share resources efficiently.
One of the most significant advantages of networks is their ability to connect people across vast distances. The internet, for instance, has revolutionized the way we communicate and access information. It has bridged geographical gaps and allowed us to connect with individuals from different parts of the world seamlessly. From social media platforms to video conferencing tools, networks have transformed how we interact with others.
In addition to connecting people, networks also facilitate the sharing of data and resources within organizations. LANs are commonly used in offices and educational institutions to enable employees or students to access shared files and printers effortlessly. This not only enhances collaboration but also improves productivity by eliminating unnecessary duplication of work.
Moreover, networks have paved the way for cloud computing—a technology that has transformed how businesses operate. Cloud computing allows organizations to store data and run applications on remote servers accessed through the internet. This eliminates the need for costly on-site infrastructure while providing scalability and flexibility.
However, with increased connectivity comes increased vulnerability. Networks are susceptible to security threats such as hacking attempts, malware infections, and data breaches. Therefore, implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect sensitive information and maintain network integrity.
Network administrators play a vital role in managing and maintaining networks effectively. They monitor network performance, troubleshoot issues promptly, ensure data backups are in place, and enforce security protocols. Their expertise ensures that networks run smoothly and securely, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency.
Looking ahead, as technology continues to evolve, networks will only become more critical. The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has led to an exponential increase in connected devices, from smart home appliances to industrial sensors. Networks will be the backbone that enables these devices to communicate and share data seamlessly.
In conclusion, networks have revolutionized the way we connect and communicate in today’s digital world. From global internet connectivity to local office networks, they have become indispensable in our daily lives. As technology advances further, networks will continue to evolve, connecting us even more closely and shaping the future of communication and collaboration.
9 Frequently Asked Questions about Networks: A Comprehensive Guide for UK Users
- How do I set up a network?
- What is the best type of network for my business?
- What are the benefits of having a network?
- How do I secure my network from hackers?
- How can I increase the speed of my network connection?
- What is an IP address and how does it work?
- How do I troubleshoot network problems?
- What is a firewall and why should I use one?
- How can I optimize my Wi-Fi signal strength?
How do I set up a network?
Setting up a network can be a complex process, but here are some general steps to help you get started:
- Determine your network requirements: Consider the purpose of your network and what devices you want to connect. Are you setting up a home network or an office network? Will you need wired or wireless connections? Understanding your requirements will guide your network setup.
- Plan your network layout: Map out the physical locations of devices and determine how they will be connected. Decide where to position routers, switches, and access points based on signal strength and coverage needs.
- Choose networking equipment: Select the necessary networking equipment based on your requirements. This typically includes a router, switch(es), and possibly wireless access points (if setting up a wireless network). Ensure that the equipment supports the desired features and has sufficient capacity for your needs.
- Connect devices: Start by connecting your router to the internet source (e.g., modem). Then, connect devices like computers, printers, or servers to the router using Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi connections according to your chosen setup.
- Configure network settings: Access your router’s administration interface via a web browser and configure basic settings such as SSID (network name), password, security protocols (WPA2 recommended), DHCP settings, and IP address allocation if needed. You may also set up port forwarding or virtual private networks (VPNs) for advanced functionality.
- Secure your network: Enable encryption (WPA2) on Wi-Fi networks with strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access. Change default login credentials for routers and other devices to enhance security.
- Test connectivity: Verify that all connected devices can communicate with each other and access the internet if required. Troubleshoot any connectivity issues by checking cable connections, restarting devices, or adjusting configurations as needed.
- Implement additional features: Depending on your needs, you may want to set up additional features like file sharing, printer sharing, or network storage. These can be configured on specific devices or through the router’s administration interface.
- Regular maintenance: Keep your network up to date by installing firmware updates for routers and other devices. Periodically review and update security settings, passwords, and access controls. Regularly monitor network performance and address any issues that arise.
Remember, setting up a network can vary depending on the complexity of your requirements and the specific equipment you are using. It may be helpful to consult documentation or seek assistance from professionals if you encounter difficulties during the setup process.
What is the best type of network for my business?
Determining the best type of network for your business depends on various factors, including the size of your organization, the nature of your operations, and your specific requirements. Here are a few common types of networks that you can consider:
- Local Area Network (LAN): LANs are typically used within a single location, such as an office building or campus. They provide fast and reliable communication between devices within a limited area. LANs are suitable for small to medium-sized businesses that need to share resources like files, printers, and internet access among employees.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): WANs connect multiple LANs across larger geographical areas, often using leased lines or internet connections. WANs are ideal for businesses with multiple branch offices that need to communicate and share data securely over long distances.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): VPNs use encryption technology to create secure connections over public networks like the internet. They allow remote employees or branch offices to access the company’s network resources securely. VPNs are particularly useful for businesses with remote workers or those requiring secure access from different locations.
- Cloud Network: Cloud networks leverage cloud computing services to store data and run applications on remote servers accessed via the internet. This type of network eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud networks are beneficial for businesses that require easy access to data from various locations and want to leverage cloud-based services.
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): WLANs use wireless technology (Wi-Fi) to connect devices within a limited area without the need for physical cables. WLANs offer mobility and flexibility in terms of device connectivity but may have limitations in terms of range and potential interference issues.
When selecting a network type, it’s important to consider factors such as scalability, security requirements, budget constraints, future growth plans, and IT infrastructure capabilities. It is often beneficial to consult with IT professionals or network specialists who can assess your specific business needs and recommend the most suitable network solution for your organization.
What are the benefits of having a network?
Having a network offers numerous benefits, both for individuals and organizations. Here are some key advantages of having a network:
- Communication and Collaboration: Networks enable seamless communication and collaboration between individuals or departments within an organization. Whether it’s sharing files, sending emails, or conducting video conferences, networks facilitate efficient and instant communication, fostering teamwork and improving productivity.
- Resource Sharing: Networks allow for the sharing of resources such as printers, scanners, and storage devices. This eliminates the need for individual devices for each user, reducing costs and promoting resource optimization.
- Data Sharing: Networks enable the easy sharing and transfer of data between connected devices. This promotes efficient workflows and eliminates the need for physical media (such as USB drives) to exchange files.
- Centralized Data Storage: Networks provide centralized data storage options, such as servers or cloud-based solutions. This ensures that data is securely stored in one location, making it easier to manage backups and access important information from multiple devices.
- Increased Efficiency: Networks streamline processes by automating tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming if done manually. For example, automated software updates can be deployed across all connected devices simultaneously, saving time and effort.
- Scalability: Networks can easily accommodate growth and expansion by adding new devices or users without significant disruption. This scalability allows businesses to adapt to changing needs quickly.
- Enhanced Security: While networks can pose security risks if not properly protected, they also offer enhanced security measures compared to standalone systems. Network administrators can implement firewalls, encryption protocols, user authentication processes, and other security measures to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Internet Access: Networks provide internet connectivity to all connected devices within an organization or home environment. This enables access to vast amounts of information online, facilitates research and learning opportunities, and supports online collaboration.
- Cost Savings: Implementing a network infrastructure can lead to cost savings in various ways. Sharing resources and centralizing data storage reduces the need for duplicate equipment. Additionally, network-based communication methods (e.g., VoIP) can be more cost-effective than traditional telephone systems.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Wireless networks offer the flexibility to connect devices without the need for physical cables, allowing users to move freely within the network’s coverage area. This promotes mobility and enables remote work options, increasing productivity and work-life balance.
In summary, networks provide a multitude of benefits, including improved communication, resource sharing, centralized data storage, increased efficiency, scalability, enhanced security measures, internet access, cost savings, and flexibility. These advantages make networks an essential component of modern-day connectivity and productivity.
How do I secure my network from hackers?
Securing Your Network from Hackers: Best Practices
In an increasingly interconnected world, network security is of paramount importance. Protecting your network from hackers requires a proactive approach and adherence to best practices. Here are some essential steps you can take to enhance the security of your network:
- Use Strong Passwords: Ensure that all devices and accounts on your network have strong, unique passwords. Avoid using common or easily guessable passwords. Consider implementing multi-factor authentication for an additional layer of security.
- Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update the firmware, operating systems, and applications on your network devices. Manufacturers often release updates that address security vulnerabilities, so staying up to date is crucial.
- Implement Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and external threats. Configure firewalls to allow only necessary incoming and outgoing traffic while blocking unauthorized access attempts.
- Enable Network Encryption: Use encryption protocols such as WPA2 or WPA3 for wireless networks to prevent unauthorized access to data transmitted over the airwaves.
- Segment Your Network: Divide your network into separate segments or VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) based on different security levels or departments within your organization. This helps contain potential breaches and limits access between segments.
- Implement Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can automatically block or alert you about potential threats in real-time.
- Regularly Backup Data: Create regular backups of critical data stored on your network devices and ensure they are securely stored off-site or in the cloud. In case of a breach, having backups will help you recover important information without paying ransom demands.
- Educate Users: Train employees on best practices for network security, such as recognizing phishing emails, avoiding suspicious websites, and not sharing sensitive information unless necessary. Regularly remind them about the importance of maintaining a secure network environment.
- Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): If remote access to your network is required, use VPNs to create secure connections between remote devices and your network. This ensures that data transmitted over the internet remains encrypted and protected.
- Monitor Network Activity: Implement network monitoring tools to track and analyze network traffic for any anomalies or suspicious behavior. This allows you to detect potential threats early and take appropriate action.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Periodically assess your network’s security posture through vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and audits conducted by external security professionals. This helps identify weaknesses that need to be addressed promptly.
- Establish Incident Response Plans: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a security breach. This will help minimize damage, facilitate timely recovery, and ensure a coordinated response.
Remember, network security is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and regular updates. By implementing these best practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your network and protect it from potential hackers.
How can I increase the speed of my network connection?
If you’re looking to increase the speed of your network connection, here are a few tips that may help:
- Check your internet plan: Ensure that you have subscribed to an internet plan that offers the desired speed. Contact your internet service provider (ISP) to inquire about available plans and consider upgrading if necessary.
- Position your router strategically: The placement of your router can significantly impact the signal strength and coverage. Place it in a central location, away from obstructions like walls or furniture, to ensure optimal coverage throughout your space.
- Reduce interference: Other electronic devices like cordless phones, microwave ovens, or baby monitors can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Keep your router away from such devices or switch to a different wireless channel to minimize interference.
- Update firmware and drivers: Regularly check for firmware updates for your router and install them as they often include performance improvements and bug fixes. Additionally, keep the drivers for your network adapters up to date on your devices.
- Use a wired connection: If possible, connect devices directly to the router using Ethernet cables instead of relying solely on Wi-Fi connections. Wired connections generally offer faster and more stable speeds.
- Limit bandwidth usage: If there are multiple devices connected to the network simultaneously, heavy bandwidth usage from one device can affect others’ speeds. Consider managing bandwidth usage by prioritizing certain applications or limiting data-intensive activities during peak hours.
- Secure your network: Unauthorized users accessing your network can slow down speeds by consuming bandwidth. Secure your Wi-Fi network with a strong password and encryption method (WPA2 is recommended).
- Clear cache and cookies: Over time, accumulated cache and cookies on devices can slow down browsing speeds. Regularly clear these temporary files from web browsers to optimize performance.
- Upgrade hardware: If you have an older router or outdated network equipment, consider upgrading them to newer models that support faster speeds and advanced technologies.
- Consult your ISP: If you’ve exhausted all options and are still experiencing slow speeds, contact your ISP to troubleshoot the issue. They may be able to identify any network problems or provide additional guidance specific to your setup.
Remember that network speeds can also be influenced by external factors such as the distance to the nearest exchange, network congestion, or limitations imposed by your ISP.
What is an IP address and how does it work?
An IP address, short for Internet Protocol address, is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. It serves as an identifier for devices within a network, enabling them to communicate and exchange data with other devices on the internet.
IP addresses are essential for routing data packets across networks. When you send or receive information over the internet, the data is divided into small packets. Each packet contains the destination IP address, allowing routers and other networking devices to direct it to the correct location.
There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6). IPv4 addresses consist of four sets of numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.0.1), while IPv6 addresses use a longer alphanumeric format (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
When you connect your device to the internet through an Internet Service Provider (ISP), it assigns your device an IP address temporarily or permanently. This can be either a dynamic IP address that changes each time you connect or a static IP address that remains constant.
IP addresses work in conjunction with other networking protocols, such as TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol). TCP/IP ensures reliable delivery of data packets by breaking them into smaller units and reassembling them at the destination.
To establish communication between devices, data is sent in packets from the source device to intermediate routers until it reaches the destination device based on its IP address. Routers use routing tables to determine the most efficient path for forwarding packets across different networks.
In addition to facilitating communication between devices, IP addresses also play a crucial role in various internet-related activities. They enable websites and servers to be accessed using domain names through DNS (Domain Name System) translation.
Moreover, IP addresses are used for network administration tasks, such as identifying and troubleshooting connectivity issues, implementing security measures, and managing network traffic.
In summary, an IP address is a unique identifier assigned to devices on a computer network. It enables communication between devices by routing data packets across networks. IP addresses are essential for internet connectivity and play a vital role in networking protocols, routing, and network administration tasks.
How do I troubleshoot network problems?
When facing network problems, troubleshooting can help identify and resolve issues effectively. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot network problems:
Identify the Problem:
– Determine if the issue is affecting a single device or multiple devices.
– Check if the problem is specific to a particular application or occurs across all applications.
Restart Devices:
– Begin by restarting your modem/router, as well as the device experiencing connectivity issues.
– Power cycling these devices can often resolve temporary glitches.
Check Physical Connections:
– Ensure that all cables (Ethernet, coaxial, etc.) are securely connected at both ends.
– Verify that Wi-Fi connections are stable and within range.
Test Connectivity:
– Use other devices to check if they experience similar network issues.
– If multiple devices are affected, it may indicate a broader network problem.
Verify Network Settings:
– Confirm that your device’s network settings are correctly configured.
– Check if DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is enabled for automatic IP address assignment.
Update Firmware/Drivers:
– Ensure that your modem/router firmware is up to date.
– Update network drivers on your computer or other devices if necessary.
Disable Firewall/Antivirus:
– Temporarily disable firewall or antivirus software to check if they are causing any conflicts with network connectivity.
Ping Test and Traceroute:
– Use the command prompt (Windows) or terminal (Mac/Linux) to run ping tests and traceroutes to specific websites or IP addresses.
This helps determine if there are any packet losses or delays along the network path.
Reset Network Settings:
– Resetting network settings on your device can often resolve configuration-related issues.
This involves resetting TCP/IP stack, DNS cache, and other related settings.
Contact Internet Service Provider (ISP):
– If you have tried the above steps and are still experiencing network problems, it may be necessary to contact your ISP.
– They can perform diagnostics on their end and assist in resolving any underlying issues.
Remember, network troubleshooting can vary depending on the specific problem and devices involved. It’s always helpful to consult device manuals or online support resources for further assistance.
What is a firewall and why should I use one?
A firewall is a security device or software that acts as a barrier between your computer network and the internet, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Its primary purpose is to protect your network from unauthorized access, malicious activities, and potential threats.
Here are a few reasons why you should use a firewall:
- Network Security: A firewall acts as the first line of defense against external threats by filtering incoming traffic. It inspects each packet of data entering your network and blocks any suspicious or potentially harmful traffic, preventing unauthorized access to your systems.
- Intrusion Prevention: Firewalls help prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to your network by blocking malicious attempts such as hacking attempts, port scanning, or denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. It analyzes network traffic patterns and identifies any abnormal behavior that may indicate an ongoing attack.
- Content Filtering: Some firewalls offer content filtering capabilities, allowing you to restrict access to certain websites or types of content based on pre-defined rules. This can help increase productivity in workplaces by blocking access to non-work-related sites or protect children from accessing inappropriate content at home.
- Application Control: Firewalls can monitor and control the use of specific applications within your network. This feature allows you to block or limit the use of certain applications that may pose security risks or consume excessive bandwidth.
- Protection against Malware: Firewalls can provide an additional layer of protection against malware infections by inspecting incoming data packets for known malware signatures or suspicious behavior. They can block infected files from entering your network, reducing the risk of spreading malware internally.
- Secure Remote Access: If you have remote workers or need to provide secure access for employees working outside the office, firewalls with Virtual Private Network (VPN) capabilities allow encrypted connections between remote devices and your internal network, ensuring secure communication over public networks like the internet.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries have specific regulatory compliance requirements for network security. Using a firewall helps meet these requirements by implementing necessary security measures and protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
In summary, using a firewall is essential for network security. It helps protect your network from unauthorized access, malicious activities, and potential threats. By implementing a firewall, you can enhance the overall security posture of your network and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your data.
How can I optimize my Wi-Fi signal strength?
Optimizing Wi-Fi Signal Strength: Tips for Better Connectivity
A strong and reliable Wi-Fi signal is essential for seamless internet connectivity and smooth browsing. If you’re experiencing slow speeds or frequent disconnections, here are some tips to help you optimize your Wi-Fi signal strength:
- Position your router strategically: The placement of your Wi-Fi router plays a significant role in signal strength. Ideally, position it in a central location within your home or office to ensure maximum coverage. Avoid placing it near walls, appliances, or other objects that may obstruct the signal.
- Avoid interference from other devices: Wireless signals can be disrupted by other electronic devices such as cordless phones, microwaves, baby monitors, and Bluetooth devices. Keep your router away from these potential sources of interference to minimize signal disruption.
- Update your router’s firmware: Router manufacturers often release firmware updates that include bug fixes and performance enhancements. Check the manufacturer’s website regularly for any available updates and install them to ensure optimal performance.
- Use the right Wi-Fi channel: Routers operate on different channels to transmit data wirelessly. If you live in an area with many nearby networks, there may be interference on the default channel. Access your router’s settings and experiment with different channels to find the one with the least interference.
- Secure your network: Unwanted users accessing your Wi-Fi network can slow down your connection speed. Enable password protection (WPA2 encryption) on your network to prevent unauthorized access.
- Reduce congestion: In crowded areas with multiple devices connected to the same network, bandwidth can become congested, leading to slower speeds for everyone. Consider limiting bandwidth-heavy activities such as video streaming or large downloads during peak usage times.
- Upgrade your equipment: If you’re using an older router or one that doesn’t support modern Wi-Fi standards (such as 802.11ac), consider upgrading to a newer model. Newer routers offer better range, faster speeds, and improved signal stability.
- Use Wi-Fi signal boosters or extenders: If you have a large home or office space with areas that receive weak Wi-Fi signals, consider using Wi-Fi signal boosters or extenders. These devices help amplify and extend the range of your existing Wi-Fi network.
- Reduce interference from neighboring networks: If you live in an apartment complex or densely populated area, neighboring Wi-Fi networks can interfere with yours. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to identify the least congested channel and adjust your router’s settings accordingly.
- Consider a mesh network system: For larger homes or spaces with multiple dead zones, a mesh network system may be beneficial. These systems consist of multiple access points strategically placed throughout the area to provide seamless coverage without signal degradation.
By following these tips, you can significantly improve your Wi-Fi signal strength and enjoy faster and more reliable internet connectivity.