Building the Future: Exploring the Vital Role of Telecommunications Network Infrastructure
Telecommunications Network Infrastructure: Building the Backbone of Connectivity
In today’s interconnected world, where communication plays a vital role in every aspect of our lives, a robust and efficient telecommunications network infrastructure is essential. From phone calls and text messages to internet browsing and video streaming, we rely on these networks to transmit information quickly and reliably. But have you ever wondered what goes into building and maintaining this intricate web of connectivity? Let’s explore the world of telecommunications network infrastructure.
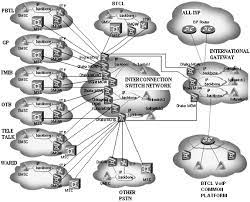
At its core, telecommunications network infrastructure refers to the physical and virtual elements that enable the transmission, routing, and delivery of voice, data, and multimedia content across vast distances. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, including wired and wireless systems, fiber optic cables, routers, switches, data centers, satellites, and much more.
The foundation of any telecommunications network infrastructure lies in its physical components. These include the cables that span across cities and countries – both underground and overhead – carrying massive amounts of data in the form of electrical signals or light pulses. Fiber optic cables have become increasingly popular due to their ability to transmit data at incredible speeds over long distances while minimizing signal loss.
To ensure seamless connectivity for users, these physical elements are interconnected through an intricate system of routers and switches. Routers direct data packets between different networks or devices while switches facilitate communication within a particular network. These devices act as traffic managers within the vast web of interconnected systems.
Data centers also play a crucial role in telecommunications network infrastructure. These facilities house servers that store vast amounts of information and provide computing power for various applications. They act as central hubs for processing data requests from users across the network.
Wireless technologies have revolutionized telecommunications by enabling mobility and ubiquitous connectivity. Mobile networks consist of base stations strategically placed to provide coverage over large areas. These base stations communicate with mobile devices using radio waves or microwaves.
The advent of 5G technology has further accelerated the growth potential for telecommunications network infrastructure. With its ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and ability to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously, 5G promises to revolutionize industries such as autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and smart cities.
However, building and maintaining a telecommunications network infrastructure is not without its challenges. It requires careful planning, investment in cutting-edge technology, and constant monitoring to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Network engineers and technicians work tirelessly behind the scenes to design, deploy, and maintain these networks while addressing issues such as congestion, signal interference, and security threats.
In conclusion, telecommunications network infrastructure forms the backbone of our modern communication ecosystem. It enables us to connect with people around the world effortlessly while facilitating the exchange of information on an unprecedented scale. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, so too will the demand for robust and efficient telecommunications networks. The future holds exciting possibilities as we strive to build even faster, more reliable networks that will shape our digital world for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions: Telecommunications Network Infrastructure
- What are the benefits of having a telecommunications network infrastructure?
- How secure is a telecommunications network infrastructure?
- What are the best practices for maintaining a telecommunications network infrastructure?
- How do I choose the right type of telecommunications network infrastructure for my business needs?
- What are the costs associated with setting up and running a telecommunications network infrastructure?
- Are there any legal or regulatory requirements that I need to be aware of when setting up my own telecommunications network infrastructure?
- How can I ensure that my telecommunications network infrastructure is future-proofed and able to keep up with advances in technology?
What are the benefits of having a telecommunications network infrastructure?
Having a robust telecommunications network infrastructure brings numerous benefits to individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Enhanced Connectivity: A well-developed telecommunications network infrastructure ensures seamless connectivity, allowing people to communicate with each other effortlessly. It enables instant communication through phone calls, text messages, emails, video conferencing, and social media platforms. This connectivity fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and efficient decision-making.
- Global Reach: Telecommunications networks transcend geographical boundaries, enabling communication and information exchange on a global scale. It facilitates international business transactions, supports remote work opportunities, and connects people from diverse backgrounds and cultures.
- Economic Growth: Telecommunications infrastructure is a catalyst for economic growth. It provides the foundation for e-commerce platforms, online marketplaces, and digital payment systems that drive commerce in the digital age. Businesses can reach wider markets and expand their customer base beyond traditional boundaries.
- Improved Access to Information: Telecommunications networks ensure rapid access to information from various sources such as news websites, educational platforms, research databases, and online libraries. This democratization of information empowers individuals with knowledge and promotes lifelong learning.
- Innovation and Technological Advancements: A strong telecommunications network infrastructure fuels innovation by providing a platform for the development of new technologies and services. It enables the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and other emerging technologies that drive progress in multiple industries.
- Efficient Public Services: Governments utilize telecommunications networks to deliver essential public services efficiently. This includes emergency response systems, telemedicine for remote healthcare access, e-government services for streamlined administrative processes, smart city initiatives for improved urban living conditions, and more.
- Social Connectivity: Telecommunications networks play a vital role in connecting people socially by facilitating communication among friends, families, communities, and interest groups across distances. They enable social networking platforms, online forums, and instant messaging apps that help maintain relationships and foster social interactions.
- Disaster Management and Resilience: During times of crisis or natural disasters, a robust telecommunications network infrastructure becomes even more critical. It allows for effective emergency communication, coordination of relief efforts, and dissemination of vital information to affected areas.
- Increased Productivity: Businesses benefit from improved productivity through efficient communication channels provided by telecommunications networks. Teams can collaborate remotely, share files, conduct virtual meetings, and access cloud-based applications that enhance workflow efficiency.
- Personal Convenience: Telecommunications networks offer convenience in various aspects of daily life. From online shopping and banking to entertainment streaming and travel bookings, individuals can access services conveniently from the comfort of their homes or on the go.
In summary, a well-developed telecommunications network infrastructure brings connectivity, economic growth, access to information, innovation opportunities, efficient public services, social connectivity, disaster resilience, increased productivity, and personal convenience. It is a fundamental pillar of modern society that empowers individuals and drives progress in all aspects of life.
How secure is a telecommunications network infrastructure?
Ensuring the security of a telecommunications network infrastructure is of paramount importance in today’s digital landscape. As these networks carry vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, financial transactions, and confidential business communications, they are a prime target for cybercriminals. However, with the right measures in place, telecommunications network infrastructure can be made highly secure. Let’s explore some key aspects of network security:
- Encryption: Encryption plays a critical role in securing data transmission across telecommunications networks. By encoding data into an unreadable format, even if intercepted by unauthorized individuals, the information remains protected. Strong encryption protocols are used to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Firewalls act as a barrier between internal networks and external threats by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. They examine packets of data to ensure they meet specific security criteria before allowing them to pass through. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) complement firewalls by actively monitoring network traffic for any suspicious or malicious activity.
- Access Control: Implementing strict access control measures is crucial to preventing unauthorized access to telecommunications networks. This includes using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls to limit access privileges based on job roles within an organization.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Keeping all network devices up to date with the latest firmware updates and security patches is essential to address any vulnerabilities that may be exploited by attackers. Regular updates help protect against known vulnerabilities and strengthen overall network security.
- Network Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of network traffic helps identify potential security breaches or anomalies in real-time. Network administrators can detect any unusual behavior or patterns that could indicate a cyber attack or attempted intrusion.
- Employee Education: Human error remains one of the most significant risks to network security. Educating employees about best practices for cybersecurity, such as avoiding suspicious emails or links and regularly updating passwords, can significantly reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.
- Incident Response and Disaster Recovery: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place is crucial for effectively responding to security incidents. This includes procedures for containment, investigation, and recovery. Regular backups and disaster recovery plans help ensure that even in the event of a breach or system failure, data can be restored quickly and efficiently.
It is important to note that network security is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring, updating, and adaptation to emerging threats. Telecom companies invest significant resources in maintaining robust security measures to protect their network infrastructure and the sensitive data transmitted through it.
While no system can be 100% secure, implementing multi-layered security measures significantly reduces the risk of successful attacks on telecommunications network infrastructure. By combining advanced technologies, regular updates, employee education, and proactive monitoring, telecom companies strive to build secure networks that safeguard data and maintain the trust of their customers.
What are the best practices for maintaining a telecommunications network infrastructure?
Maintaining a telecommunications network infrastructure requires a proactive approach to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and security. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Regular Monitoring and Maintenance: Implement a comprehensive monitoring system to proactively identify and address any issues or anomalies in the network. This includes monitoring network traffic, bandwidth utilization, equipment health, and performance metrics. Regular maintenance tasks such as firmware updates, patch management, and equipment inspections should also be scheduled.
- Redundancy and Resilience: Build redundancy into the network infrastructure by implementing backup systems, redundant power supplies, and multiple data paths. This helps minimize downtime in case of equipment failures or natural disasters. Employing failover mechanisms ensures that traffic is automatically rerouted to alternate paths when necessary.
- Security Measures: Cybersecurity is of utmost importance in maintaining a telecommunications network infrastructure. Implement robust security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encryption protocols to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments should be conducted to identify any potential weaknesses.
- Capacity Planning: Continuously monitor network usage trends and plan for future growth accordingly. This involves assessing bandwidth requirements, upgrading equipment when necessary, and optimizing network configurations to accommodate increasing demands.
- Documentation and Asset Management: Maintain accurate documentation of the entire network infrastructure, including equipment inventory, configurations, IP addresses, cabling diagrams, and network topology maps. This documentation aids in troubleshooting efforts and facilitates efficient management of the infrastructure.
- Training and Knowledge Transfer: Provide regular training sessions for network administrators and technicians to keep them updated with the latest technologies, best practices, and industry standards. Encourage knowledge sharing within the team to ensure a collective understanding of the infrastructure’s intricacies.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that outlines procedures for recovering from major disruptions such as natural disasters or cyber attacks. Regularly test these plans through simulated scenarios to identify any weaknesses and make necessary improvements.
- Vendor Management: Maintain good relationships with vendors and service providers, ensuring clear communication channels and prompt response times. Regularly review service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure compliance and assess the performance of vendors.
- Regular Performance Analysis: Analyze network performance data to identify potential bottlenecks, areas for improvement, and opportunities for optimization. This can involve analyzing network traffic patterns, latency measurements, and Quality of Service (QoS) metrics.
- Stay Updated with Technological Advancements: Keep abreast of emerging technologies and industry trends that could enhance the network infrastructure’s performance and capabilities. Evaluate new solutions and consider their potential benefits before implementing them into the existing infrastructure.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure that their telecommunications network infrastructure remains robust, reliable, secure, and capable of meeting the evolving needs of users in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
How do I choose the right type of telecommunications network infrastructure for my business needs?
Choosing the right type of telecommunications network infrastructure for your business needs is crucial to ensure seamless connectivity, optimal performance, and scalability. Here are some factors to consider when making this decision:
- Bandwidth Requirements: Assess your business’s bandwidth requirements based on the number of employees, data usage patterns, and the types of applications you use. Consider whether you need high-speed internet access, video conferencing capabilities, or large data transfers.
- Scalability: Consider the future growth and expansion plans of your business. Will your network infrastructure be able to accommodate increased demand for bandwidth and connectivity as your business grows? Look for solutions that offer scalability and flexibility to adapt to changing needs.
- Reliability: Evaluate the reliability and uptime guarantees of different network infrastructure options. Downtime can result in significant disruptions to your business operations, so choose a solution with redundant systems, backup power supplies, and robust disaster recovery mechanisms.
- Security: Cybersecurity should be a top priority when selecting a telecommunications network infrastructure. Ensure that the solution includes robust security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption protocols, and regular security updates.
- Budget: Consider your budget constraints while evaluating different options. Compare the costs associated with installation, maintenance, upgrades, and ongoing support for each type of infrastructure.
- Wired vs. Wireless: Determine whether wired or wireless solutions best suit your business needs. Wired networks provide higher speeds and more reliable connections but may require extensive cabling installations. Wireless networks offer mobility but may have limitations in terms of coverage or potential signal interference.
- Network Management: Consider how you plan to manage and monitor your network infrastructure. Evaluate whether you have in-house expertise or if you would prefer outsourcing network management services to a third-party provider.
- Industry-Specific Requirements: Some industries have specific regulatory or compliance requirements that impact their choice of telecommunications network infrastructure (e.g., healthcare or finance). Ensure that the solution you choose meets any industry-specific standards or regulations.
- Vendor Reputation: Research and evaluate the reputation and track record of different vendors or service providers. Read reviews, seek recommendations, and inquire about their customer support services to ensure a reliable partnership.
- Consultation: If you are unsure about the best telecommunications network infrastructure for your business needs, consider consulting with experts in the field. They can provide valuable insights and help tailor a solution that aligns with your specific requirements.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right type of telecommunications network infrastructure that best suits your business needs.
What are the costs associated with setting up and running a telecommunications network infrastructure?
Setting up and running a telecommunications network infrastructure involves various costs that can vary depending on factors such as the scale of the network, technology choices, geographical coverage, and regulatory requirements. Here are some common costs associated with setting up and running a telecommunications network infrastructure:
- Infrastructure Deployment: The initial cost involves deploying the physical infrastructure, including laying fiber optic cables, installing base stations for wireless networks, setting up data centers, and acquiring land or rights-of-way for infrastructure placement.
- Equipment and Hardware: This includes the purchase or lease of networking equipment such as routers, switches, servers, antennas, transmission equipment, power systems, cooling systems, and other necessary hardware components.
- Spectrum Licensing: For wireless networks like mobile or broadband services, acquiring spectrum licenses from regulatory authorities often involves significant costs. These licenses grant exclusive rights to use specific frequency bands for communication purposes.
- Network Planning and Design: Network planning requires expertise in designing an efficient network layout that optimizes coverage and capacity while minimizing interference and signal degradation. Costs may include hiring network engineers or consultants to design the network architecture.
- Installation and Commissioning: Once the physical infrastructure is in place, there are costs associated with installing and commissioning the equipment at various locations within the network. This includes labor costs for technicians to configure devices, test connectivity, and ensure proper functionality.
- Ongoing Operations and Maintenance: Running a telecommunications network involves continuous operational expenses such as energy consumption for powering equipment, regular maintenance activities to ensure optimal performance and reliability of infrastructure components (e.g., preventive maintenance or repairs), software updates for security patches or feature enhancements, monitoring systems for fault detection and troubleshooting.
- Connectivity Costs: Telecommunications providers often have agreements with other networks or internet service providers (ISPs) to establish connectivity between different parts of their network or to provide access to the internet. These interconnection fees or transit costs can be significant depending on traffic volume.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements often comes with costs, such as fees for obtaining necessary licenses, meeting security and privacy standards, and adhering to data protection regulations.
- Staffing and Training: Building and operating a telecommunications network infrastructure requires skilled personnel to manage network operations, perform maintenance tasks, monitor performance, handle customer support, and address technical issues. Costs include salaries, training programs, and ongoing professional development.
It’s important to note that the costs associated with setting up and running a telecommunications network infrastructure can be substantial. They may vary significantly depending on the scope of the network deployment, technology choices, geographical factors, competition in the market, and other relevant factors. Careful financial planning and cost analysis are crucial for successful network implementation and long-term sustainability.
Are there any legal or regulatory requirements that I need to be aware of when setting up my own telecommunications network infrastructure?
When setting up your own telecommunications network infrastructure, it is crucial to be aware of the legal and regulatory requirements in your jurisdiction. These requirements may vary depending on the country or region you operate in. While I can provide some general information, it is essential to consult with legal experts or regulatory authorities specific to your location for accurate and up-to-date guidance. Here are a few aspects to consider:
- Licensing and Permits: In many jurisdictions, telecommunications operators are required to obtain licenses or permits from regulatory bodies before operating a network. These licenses may specify the scope of services you can offer, frequency bands you can use, and any associated fees.
- Spectrum Allocation: Wireless networks rely on allocated radio frequency spectrum for operation. Depending on your country’s regulations, you may need to acquire spectrum licenses or participate in auctions to gain access to specific frequency bands.
- Data Privacy and Security: Telecommunications networks handle vast amounts of sensitive customer data. It is crucial to comply with data protection laws and ensure proper security measures are in place to safeguard personal information from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Interconnection and Access: Some jurisdictions have regulations that require network operators to provide interconnection and access services to other providers on fair terms. These regulations aim to promote competition and ensure equal access for all participants in the telecommunications market.
- Consumer Protection: Laws governing consumer rights and protection may apply when providing telecommunications services. These laws often include provisions related to billing transparency, quality of service, dispute resolution mechanisms, and customer complaint handling procedures.
- Emergency Services: Telecommunications providers typically have obligations concerning emergency service accessibility, including providing access numbers (such as 911) for emergency calls and location identification capabilities for mobile devices.
- Infrastructure Deployment Regulations: Depending on your jurisdiction, there may be specific regulations regarding the installation of physical infrastructure such as antennas, towers, or fiber optic cables. Compliance with local zoning laws, environmental regulations, and health and safety requirements may be necessary.
- Universal Service Obligations: Some countries impose obligations on telecommunications operators to ensure universal access to essential services, particularly in underserved areas. These obligations may involve providing services to remote or economically disadvantaged regions.
It is crucial to engage legal counsel or regulatory experts who specialize in telecommunications law to navigate the specific legal and regulatory landscape in your jurisdiction. They can guide you through the process of obtaining necessary licenses, complying with regulations, and ensuring your network infrastructure meets all legal requirements.
How can I ensure that my telecommunications network infrastructure is future-proofed and able to keep up with advances in technology?
Ensuring that your telecommunications network infrastructure is future-proofed requires careful planning, foresight, and a proactive approach to technology advancements. Here are some key considerations to help you keep up with advances in technology:
- Scalability: Design your network infrastructure with scalability in mind. Anticipate future growth and ensure that your infrastructure can easily accommodate increasing demands for bandwidth, data capacity, and user connections. This may involve investing in scalable hardware and software solutions that can be expanded or upgraded as needed.
- Flexibility: Embrace technologies that offer flexibility and adaptability. Look for software-defined networking (SDN) solutions that allow you to dynamically configure and manage network resources based on changing needs. This flexibility will enable you to quickly adapt to new technologies and services without significant disruptions.
- Embrace Cloud Services: Leverage cloud-based services for certain aspects of your infrastructure. Cloud computing offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and the ability to rapidly deploy new services or applications. By migrating certain functions or data storage to the cloud, you can reduce the burden on your own infrastructure while benefiting from the agility and scalability of cloud providers.
- Stay Informed about Technology Trends: Keep abreast of emerging technologies, industry standards, and best practices through continuous learning and engagement with industry experts. Attend conferences, seminars, or webinars related to telecommunications to stay informed about the latest advancements in networking technologies.
- Invest in Network Security: As technology evolves, so do security threats. Ensure that your network infrastructure incorporates robust security measures to protect against cyber threats such as hacking attempts, data breaches, or malware attacks. Implement encryption protocols, firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and regularly update security patches.
- Collaboration with Technology Partners: Establish partnerships with reputable technology vendors or service providers who specialize in telecommunications infrastructure solutions. Collaborating with experts can provide insights into emerging technologies and help you make informed decisions about upgrading or expanding your network infrastructure.
- Regular Assessments and Upgrades: Conduct periodic assessments of your network infrastructure to identify potential bottlenecks, performance issues, or areas that may need upgrading. Regularly review your hardware, software, and security measures to ensure they align with current and future requirements.
- Future-Proofing Roadmap: Develop a strategic roadmap that outlines your long-term goals and plans for technology adoption. This roadmap should consider emerging technologies, business objectives, and potential industry trends. Regularly revisit and update this roadmap to stay aligned with the evolving technology landscape.
By incorporating these considerations into your telecommunications network infrastructure strategy, you can increase its longevity, adaptability, and ability to keep pace with advances in technology. Remember that future-proofing is an ongoing process that requires continuous evaluation, adaptation, and investment in cutting-edge solutions.